SIMD instructions in GCC
- How I learned to stop worrying and love Moore’s law
Early CPU architectures
- Intel 8080
- 5 GP registers
- common instructions 4, 5, 7, 10, or 11 cycles
- CPU clock frequency 2MHz to 3.125MHz
How to make such beast faster?
- use better MOS technology -> higher CPU clock frequency
- faster execution (fast multiplier), but nothing fancy
- superscalar architecture (multiple execution lines)
- SIMD
- too much cost (chip area, # transistors)
- to be used later
- now used everywhere
- MISD
- too complicated
- WLIW architecture
- very efficient
- needs optimizing compiler
- not backward compatible
- split instruction execution into multiple stages
- cost efficient
- => classic RISC pipeline - 5 stages
- use multiple cores
- even more costly than SIMD
- cache coherency?
- switching
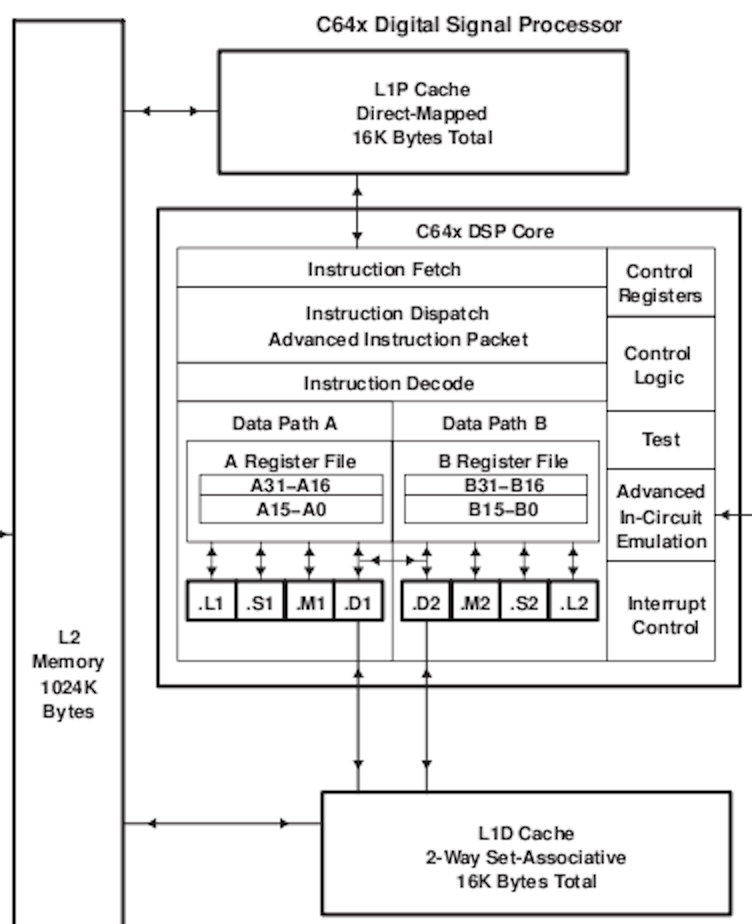
SIMD
- single instruction, multiple data
- many real-world algorithms process vectors, not scalars
- audio
- imaging
- video
- 3D graphics (to some level)
- most technical and scientific computations
- linear algebra, matrices etc.
- analysis (economy, investment, …)
- possible speedup: huge!
- and still simple enough compared to multiple cores solution
- can be used with RISC pipeline
Typical SIMD operations
- vector add/sub, multiply vector items, divide etc.
- dot product
- inversion
- add/sub without overflow (with saturation)
- shuffling
- packing/unpacking
An example - image manipulations
- saturation arithmetic



SIMD on x86(64)
MMX 1996
3DNow! 1998
SSE 1999
SSE2 2001
SSE3 2004
SSSE3 2006
SSE4 2006
SSE5 2007
AVX 2008
F16C 2009
XOP 2009
FMA4 2011
FMA3 2012
AVX2 2013
AVX-512 2015
AMX 2022
SIMD or RISC CPUs
MAX-1 Multimedia Acceleration eXtensions v1 HP-PA RISC
MAX-2 Multimedia Acceleration eXtensions v2 HP-PA RISC
VIS 1 Visual Instruction v1 Set SPARC V9
VIS 2 Visual Instruction v2 Set SPARC V9
AltiVec (obchodní názvy Velocity Engine, VMX) PowerPC
MDMX MIPS Digital Media eXtension (MaDMaX) MIPS
MIPS-3D MIPS-3D MIPS
MVI Motion Video Instructions DEC Alpha
NEON Advanced SIMD Cortex (ARMv7, ARMv8)
Packed SIMD Packed SIMD RISC-V
Vector Set Vector Set RISC-V
SVE Scalable Vector Extension ARMv8.2-A and newer
Babylon? Chaos?
- many SIMD implementations
- many possible vector formats
- integers vs. floats
- no representation in C (Go, …) syntax
Solutions?
- intrinsics
- vector extension (GCC)
Vector extension (GCC)
- based on “special” typedefs
- constructor
- accesing vector items
- all arithmetic, logical etc. operations in vectorised format
Practical part
“special” typedefs
#include <stdio.h>
typedef unsigned short int v16us __attribute__((vector_size(16)));
int main(void)
{
printf("scalar: %ld bytes\n", sizeof(unsigned short int));
printf("vector: %ld bytes\n", sizeof(v16us));
return 0;
}
Vector size, number of elements
#include <stdio.h>
typedef unsigned char v16ub __attribute__((vector_size(16)));
typedef unsigned short int v16us __attribute__((vector_size(16)));
typedef unsigned int v16ui __attribute__((vector_size(16)));
typedef unsigned long int v16ul __attribute__((vector_size(16)));
int main(void)
{
printf("unsigned char: %ld bytes\n", sizeof(unsigned char));
printf("unsigned short: %ld bytes\n", sizeof(unsigned short int));
printf("unsigned int: %ld bytes\n", sizeof(unsigned int));
printf("unsigned long: %ld bytes\n", sizeof(unsigned long int));
printf("vector unsigned char: %ld bytes\n", sizeof(v16ub));
printf("vector unsigned short: %ld bytes\n", sizeof(v16us));
printf("vector unsigned int: %ld bytes\n", sizeof(v16ui));
printf("vector unsigned long: %ld bytes\n", sizeof(v16ul));
return 0;
}
Vector add
#include <stdio.h>
typedef signed char v16ub __attribute__((vector_size(16)));
typedef signed short int v16us __attribute__((vector_size(16)));
typedef signed int v16ui __attribute__((vector_size(16)));
typedef signed long int v16ul __attribute__((vector_size(16)));
int main(void)
{
{
v16ub x = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
v16ub y = { 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff };
v16ub z = x + y;
}
{
v16us x = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
v16us y = { 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff };
v16us z = x + y;
}
{
v16ui x = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
v16ui y = { 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff };
v16ui z = x + y;
}
{
v16ul x = { 1, 2 };
v16ul y = { 0xff, 0xff };
v16ul z = x + y;
}
return 0;
}
Accessing vector items
#include <stdio.h>
typedef unsigned short int v16us __attribute__((vector_size(16)));
int main(void)
{
v16us x = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
v16us y = { 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff };
v16us z = x + y;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
printf("%d %d\n", i, z[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Vector is not an array!
typedef float v1024f __attribute__((vector_size(1024)));
void addVectors(v1024f * x, v1024f * y, v1024f * z)
{
*z = *x + *y;
}
int main(void)
{
v1024f x = { 1.0 };
v1024f y = { 1.0 };
v1024f z;
addVectors(&x, &y, &z);
return 0;
}
Let’s look into assembly
#include <stdio.h>
typedef signed char v16ib __attribute__((vector_size(16)));
void add16ib(v16ib x, v16ib y, v16ib * z)
{
*z = x + y;
}
void sub16ib(v16ib x, v16ib y, v16ib * z)
{
*z = x - y;
}
void mul16ib(v16ib x, v16ib y, v16ib * z)
{
*z = x * y;
}
void div16ib(v16ib x, v16ib y, v16ib * z)
{
*z = x / y;
}
void mod16ib(v16ib x, v16ib y, v16ib * z)
{
*z = x % y;
}
void and16ib(v16ib x, v16ib y, v16ib * z)
{
*z = x & y;
}
void or16ib(v16ib x, v16ib y, v16ib * z)
{
*z = x | y;
}
void xor16ib(v16ib x, v16ib y, v16ib * z)
{
*z = x ^ y;
}
void rshift16ib(v16ib x, v16ib y, v16ib * z)
{
*z = x >> y;
}
void lshift16ib(v16ib x, v16ib y, v16ib * z)
{
*z = x << y;
}
void print_vectors(const char *message, const char *op, v16ib * x,
v16ib * y, v16ib * z)
{
int i;
puts(message);
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(v16ib) / sizeof(signed char); i++) {
printf("%2d %d %s %d = %d\n", i, (*x)[i], op, (*y)[i], (*z)[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
int main(void)
{
v16ib x;
v16ib y;
v16ib z;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(v16ib) / sizeof(signed char); i++) {
x[i] = i * 2;
y[i] = 16 - i;
}
add16ib(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector addition", "+", &x, &y, &z);
sub16ib(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector subtraction", "-", &x, &y, &z);
mul16ib(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector multiply", "*", &x, &y, &z);
div16ib(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector divide", "/", &x, &y, &z);
mod16ib(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector modulo", "%", &x, &y, &z);
and16ib(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector bitwise and", "&", &x, &y, &z);
or16ib(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector bitwise or", "|", &x, &y, &z);
xor16ib(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector bitwise xor", "^", &x, &y, &z);
rshift16ib(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector right shift", ">>", &x, &y, &z);
lshift16ib(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector left shift", "<<", &x, &y, &z);
return 0;
}
Floats and doubles
#include <stdio.h>
typedef float v16float __attribute__((vector_size(16)));
void add16float(v16float x, v16float y, v16float * z)
{
*z = x + y;
}
void sub16float(v16float x, v16float y, v16float * z)
{
*z = x - y;
}
void mul16float(v16float x, v16float y, v16float * z)
{
*z = x * y;
}
void div16float(v16float x, v16float y, v16float * z)
{
*z = x / y;
}
void print_vectors(const char *message, const char op, v16float * x,
v16float * y, v16float * z)
{
int i;
puts(message);
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(v16float) / sizeof(float); i++) {
printf("%2d %5.3f %c %5.3f = %5.3f\n", i, (*x)[i], op, (*y)[i],
(*z)[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
int main(void)
{
v16float x;
v16float y;
v16float z;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(v16float) / sizeof(float); i++) {
x[i] = i;
y[i] = i + 0.1;
}
add16float(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector addition", '+', &x, &y, &z);
sub16float(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector subtraction", '-', &x, &y, &z);
mul16float(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector multiply", '*', &x, &y, &z);
div16float(x, y, &z);
print_vectors("vector divide", '/', &x, &y, &z);
return 0;
}